
In cases where OI type 2 overlaps with OI type 3, Therefore, it becomes imperative to makeĪ precise intrauterine diagnosis of OI type 2 to suggest pregnancy With OI type 2 (by ultrasound and DNA analysis) results in In developed countries, most children’s prenatal diagnosis Sequencing (NGS) decrease the need for phenotyping? Genetic diagnosing, and will molecular techniques such as NextGeneration How vital is phenotyping of individuals compared to molecular How significant can be a possible misclassification of OI In general, glycine substitutions near the carboxylterminalĮnd appear to result in the severest phenotype. To heterozygous COL1A1/2 mutations that result in substitutionsįor glycine. Types 2 and 3 are dominantly inherited, and most cases are due The distinction between these patients and those with a milderįorm of perinatally lethal OI type 2 might be difficult. Of cases with severe deformity and normal sclerae have OI typeģ. With progressively deforming OI, and probably only a proportion Īdditionally, the OI type 3 phenotype does not necessarily equate Type 2-B), and as such, they can show overlap with OI type 3. Phenotype which is a little less severe with fewer rib fractures (OI Since 1984 it has been postulated that some babies have a To the provided pedigree, the asymptomatic parents are nonconsanguineous,Īnd she has no affected sibling a de novo gene mutation was suspected. Imperfecta Type 2 is generally considered lethal.

(Gly1012Ser), aĭefect compatible with OI type 2 as well as OI type 3. Gene, chromosome 7, exon 46 c.3034GC>A:p. Mutation with autosomal dominant inheritance in the COL1A2 Weĭecided to proceed with genetic testing for OI in order to haveĪ precise molecular diagnosis. Laboratory tests were all within normal limits. Malformations, some of which had been treated surgically (FigureġA and B). Radiographic investigation revealed severe
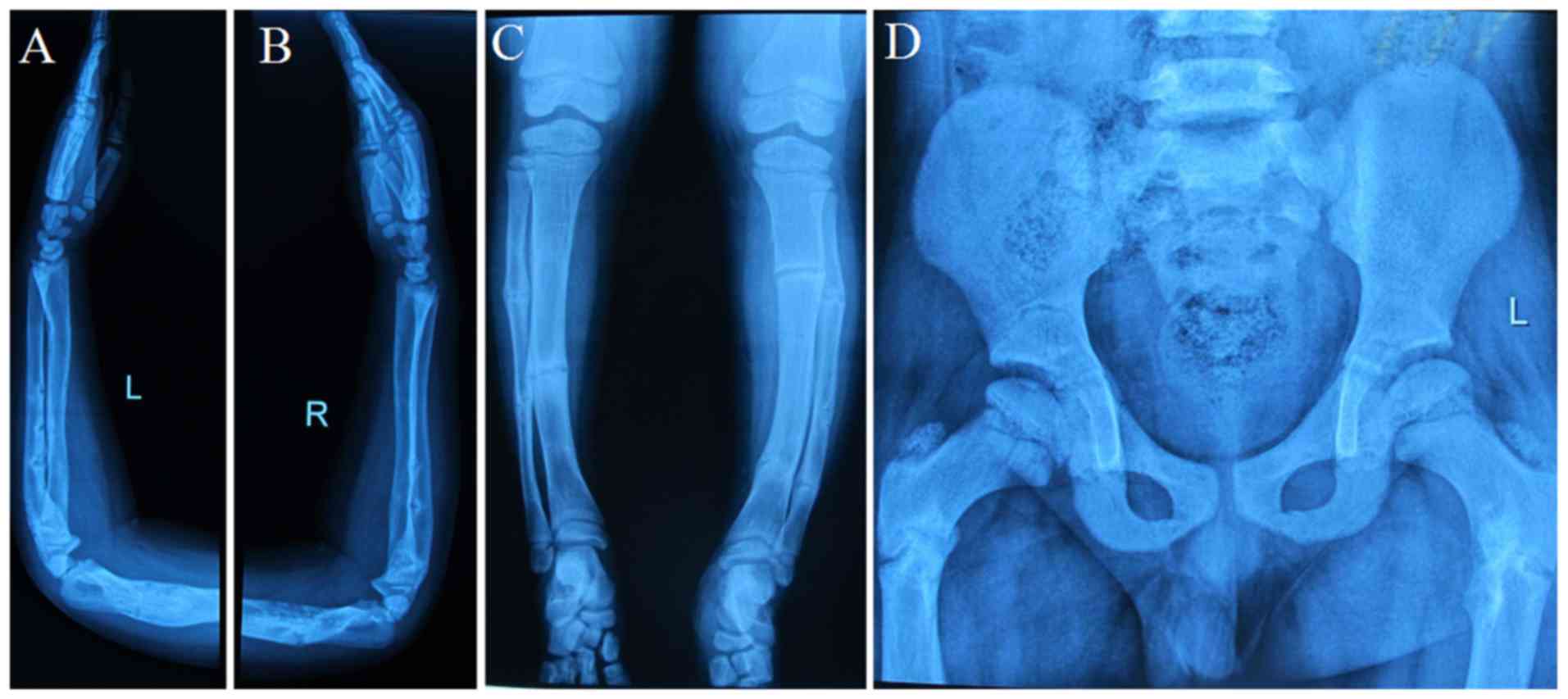
Revealed severe malformations, some of which had been treatedīone mass density (L1-L4) was measured 0.62 g/cm 3 withĪ Z-score of -3.8. The patient was mobilizing both withĪ cane and a wheelchair alternatively. (OI), type 3 (progressively deforming OI). This point, she was treated based on the clinical manifestationsĪccording to Sillence classification of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Sociology and a current student at the Art School of Acting. Hip) as well as severe scoliosis, poor hearing, blue sclera, andĭentinogenesis imperfecta. She reported a history of multiple spontaneous skeletalįractures since the 8th day of birth (humoral, rib, femoral and A 36-year-old woman sought consultation for low boneĭensity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
